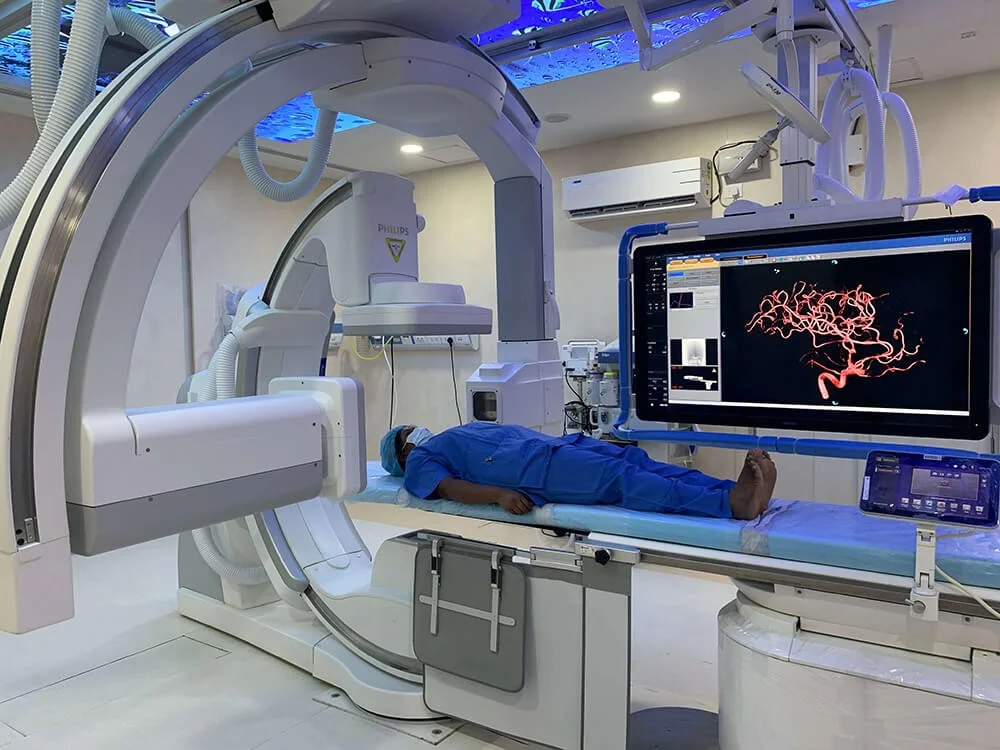
Interventional Radiology (IR) uses real-time imaging such as X-ray, ultrasound, CT, or MRI to guide tiny instruments through the body for treatment — without large surgical incisions.
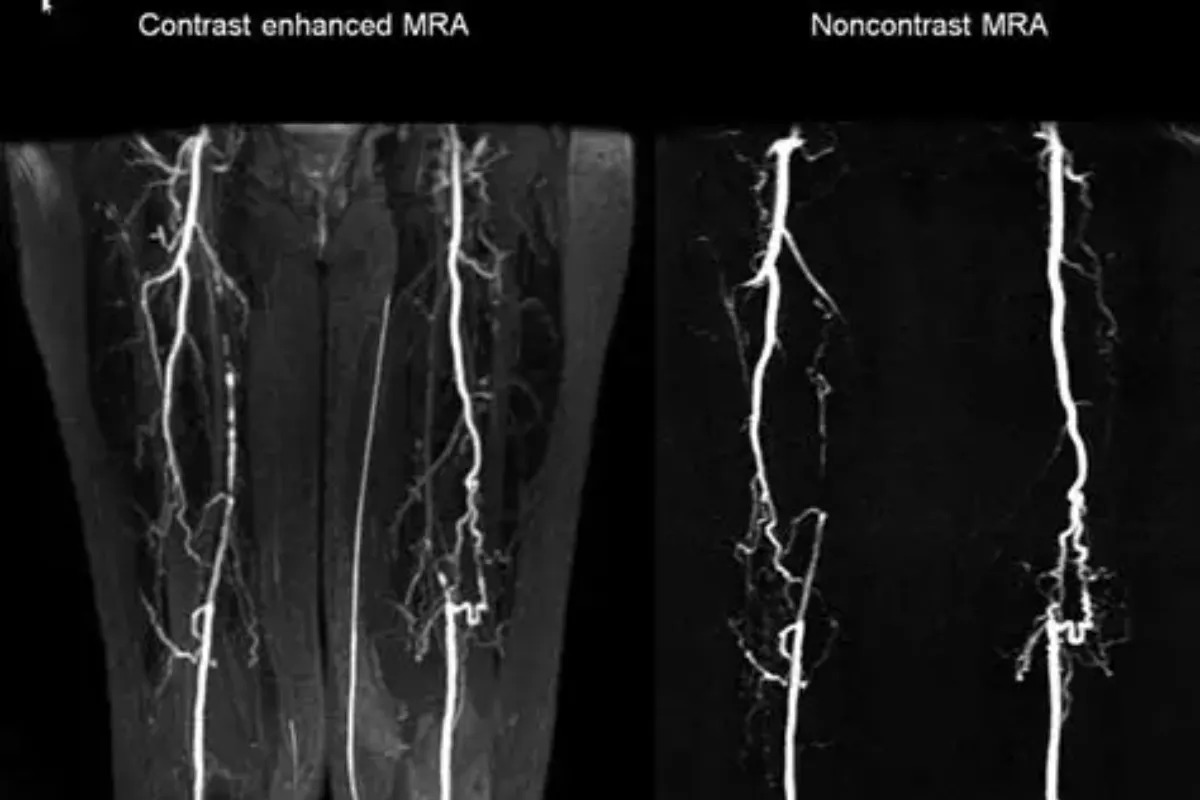
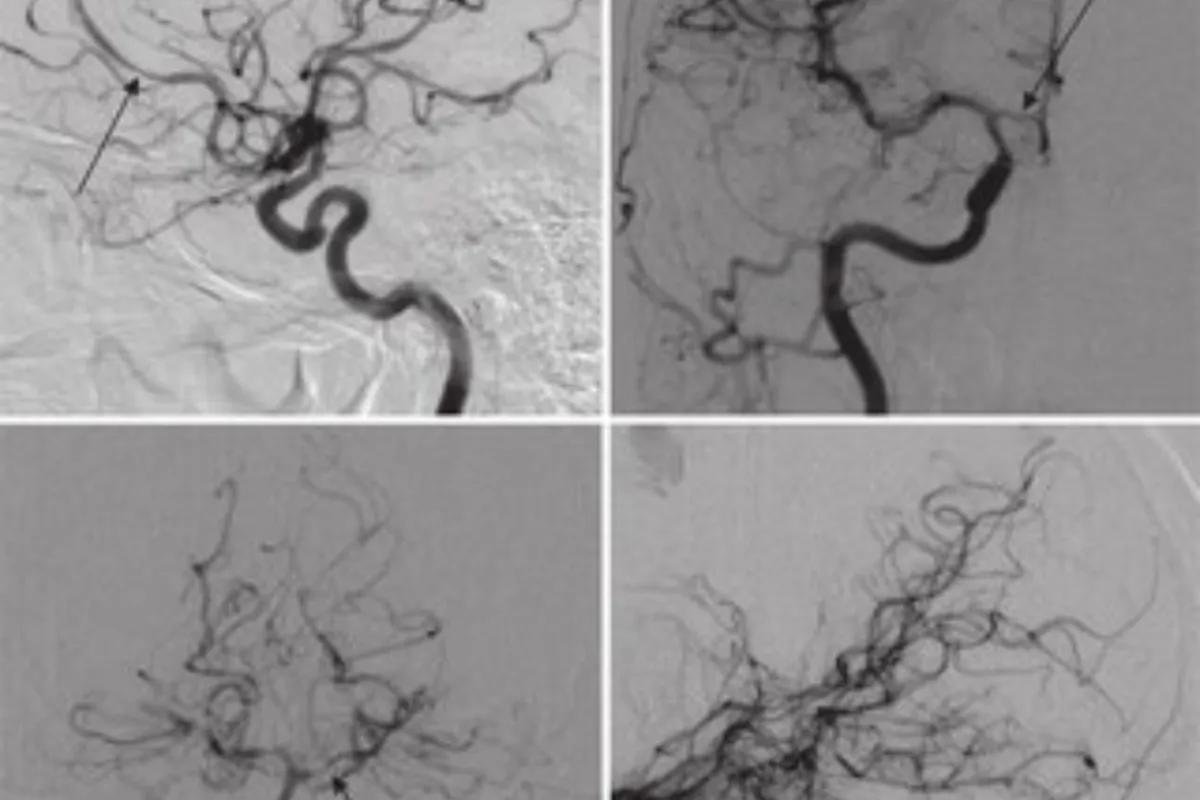
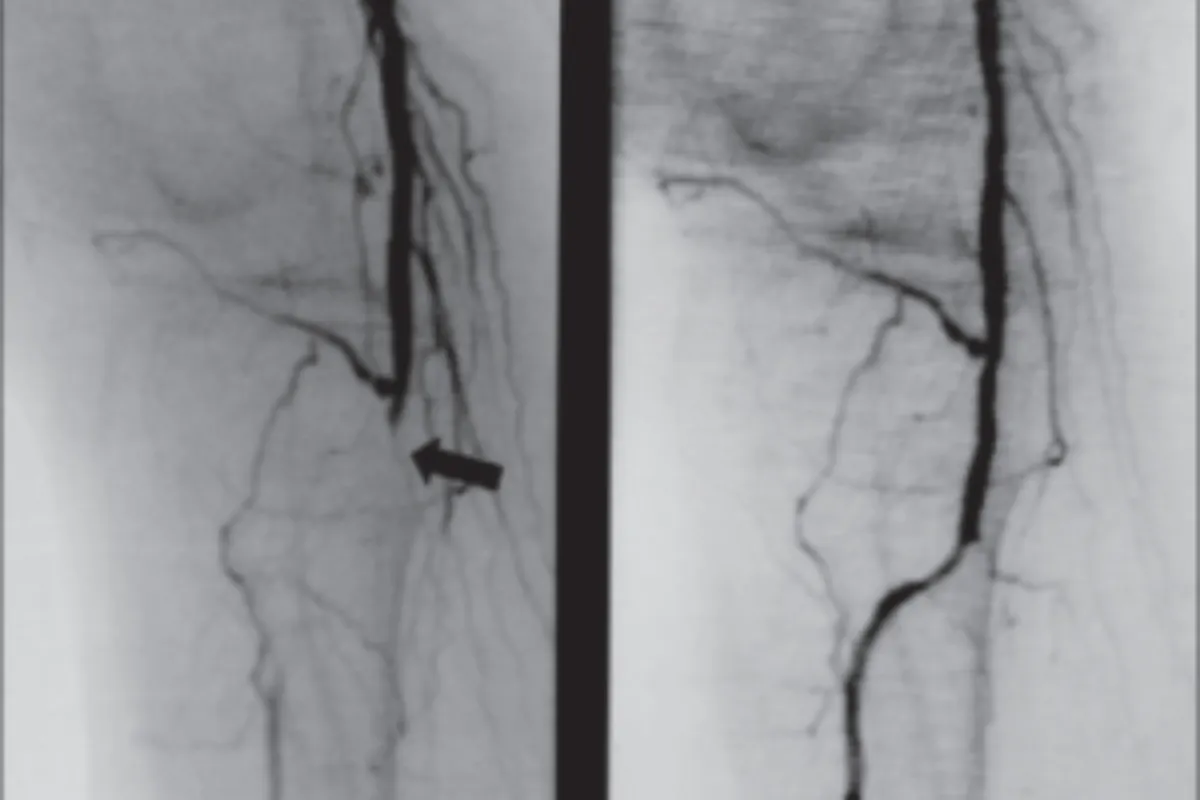
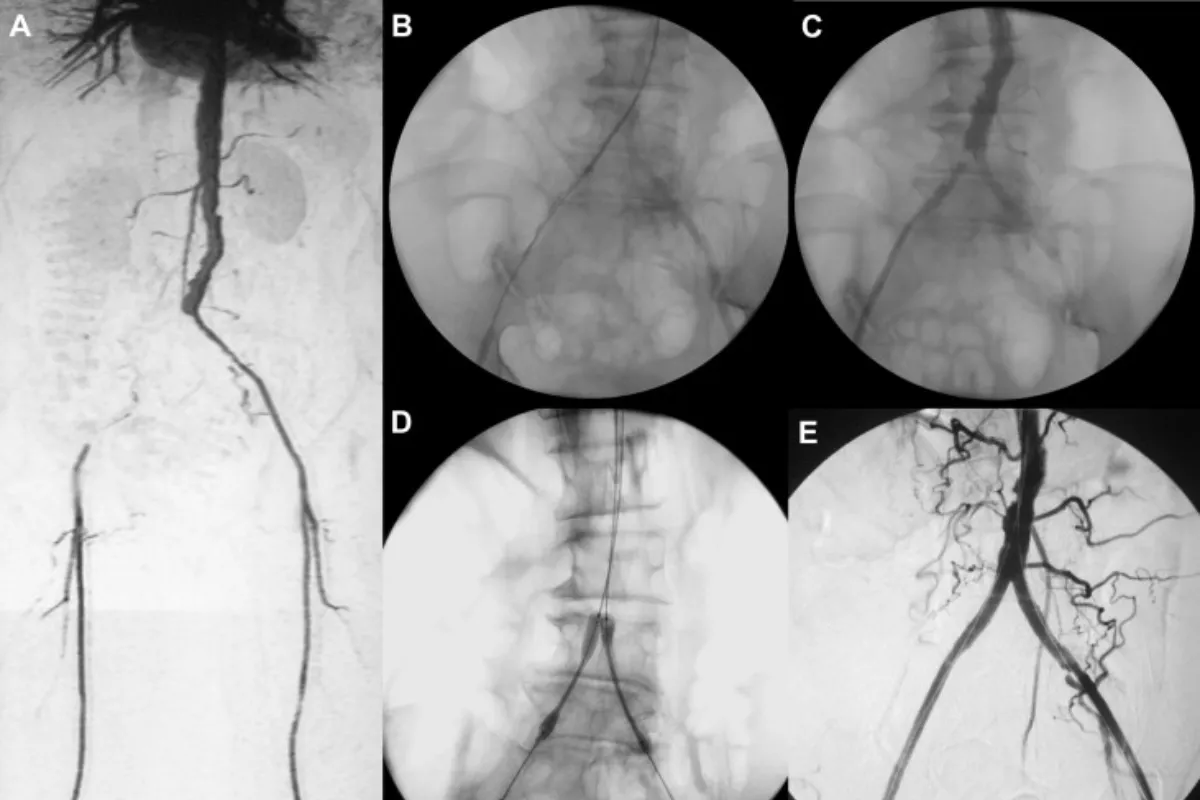
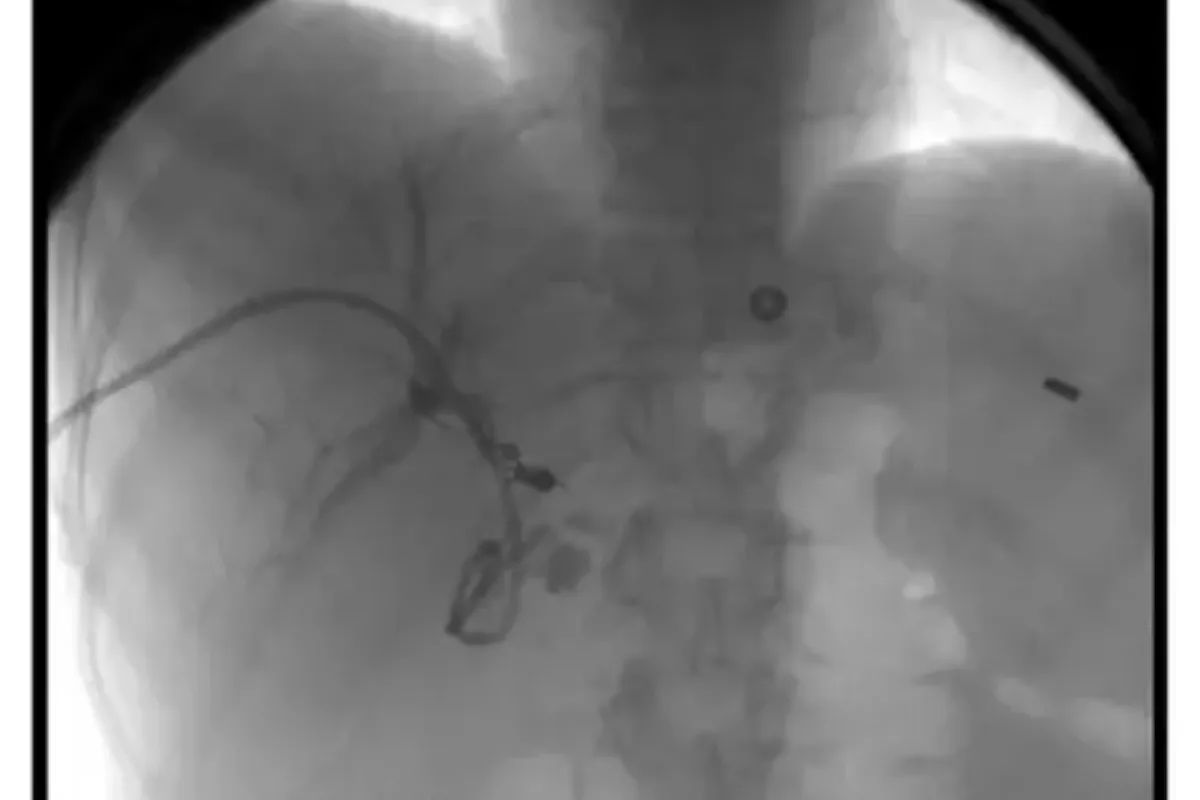
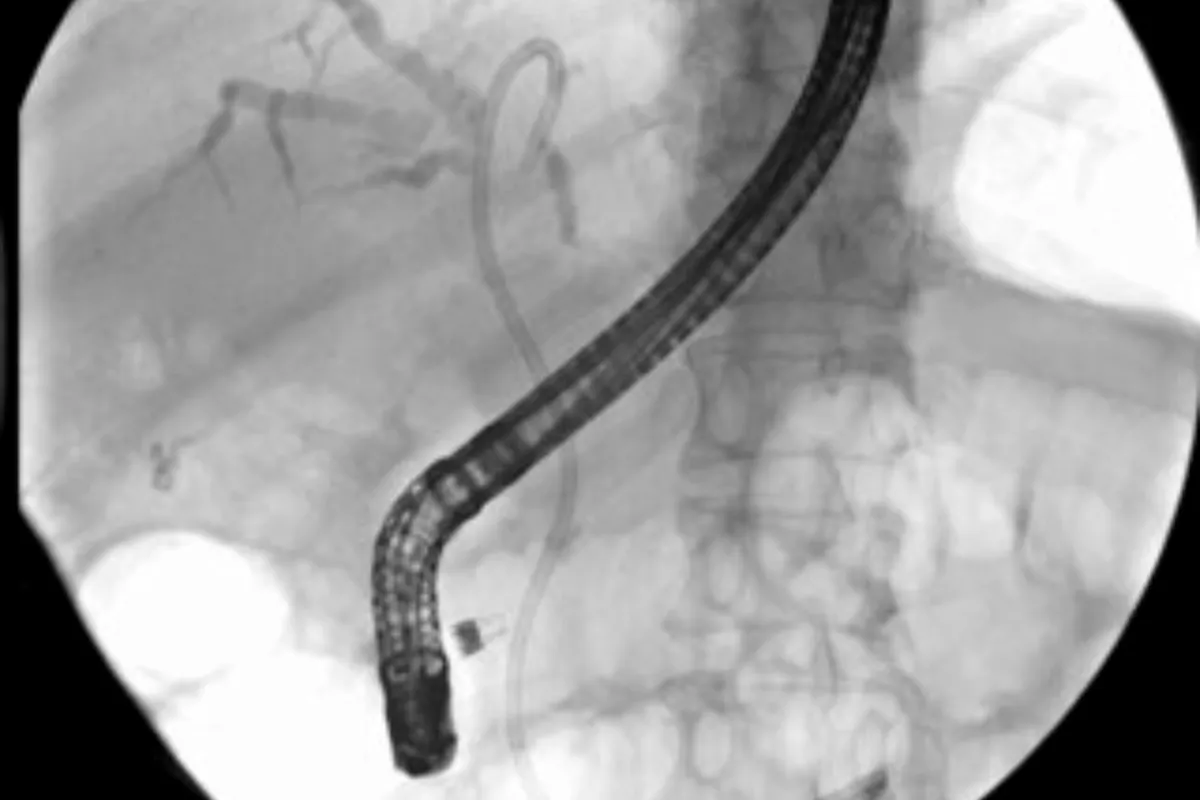
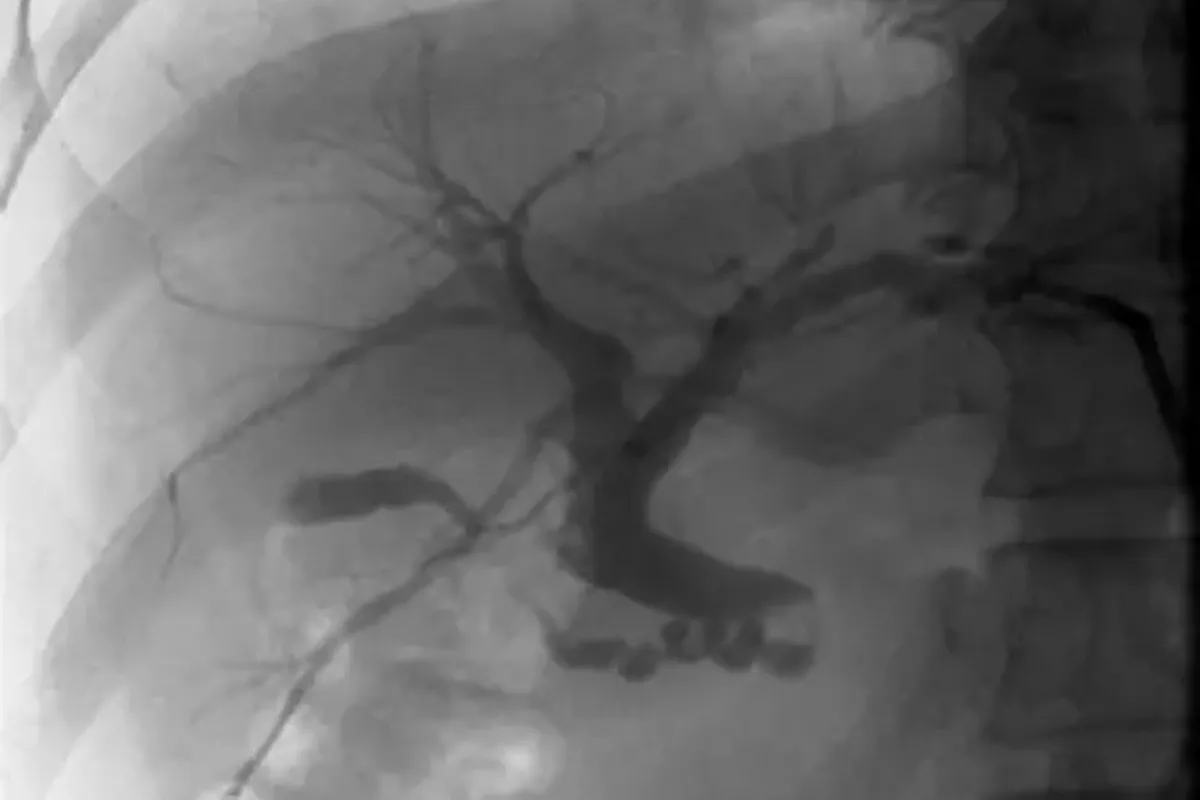
These are minimally invasive procedures used to treat gastric varices by blocking abnormal veins to prevent bleeding. They improve blood flow patterns, reduce the risk of rebleeding, and are effective alternatives when TIPS is not suitable.
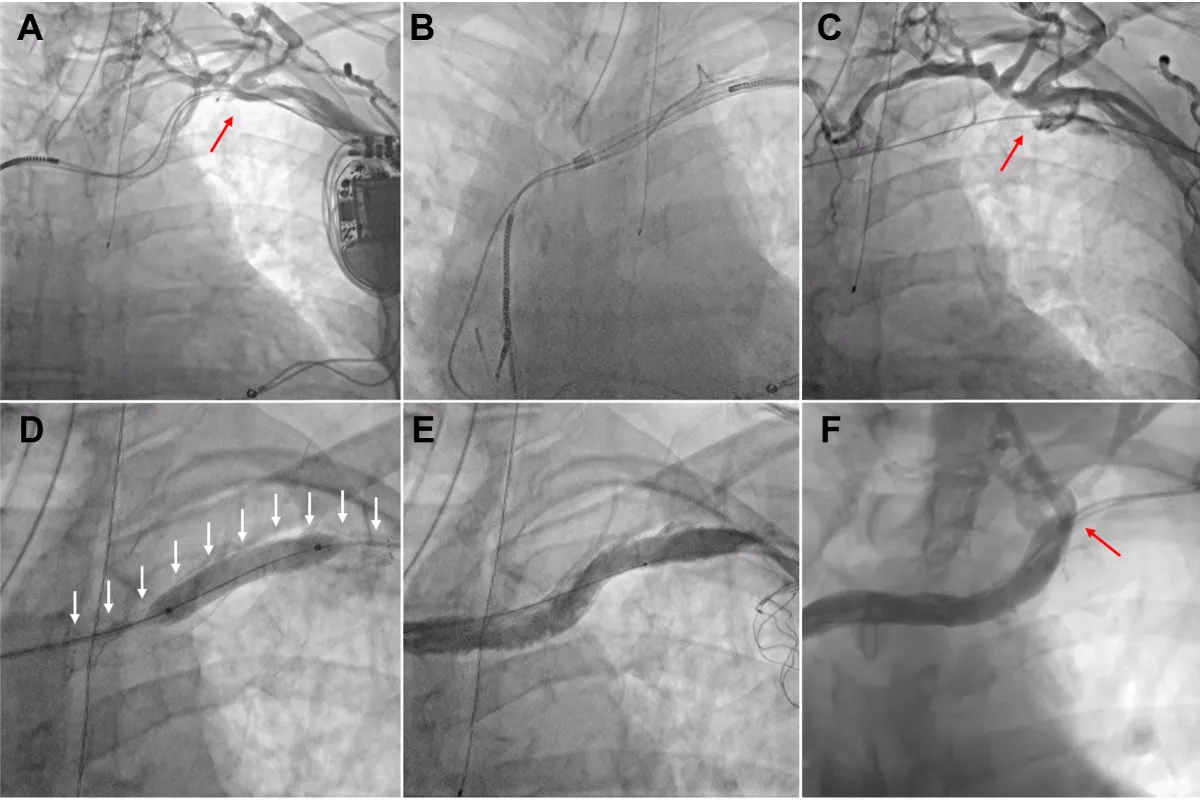
These are endovascular procedures done to open narrowed or blocked veins in the liver (hepatic veins), inferior vena cava (IVC), or superior vena cava (SVC). By restoring proper blood flow, they relieve symptoms like swelling, breathlessness, or liver congestion and prevent further complications.
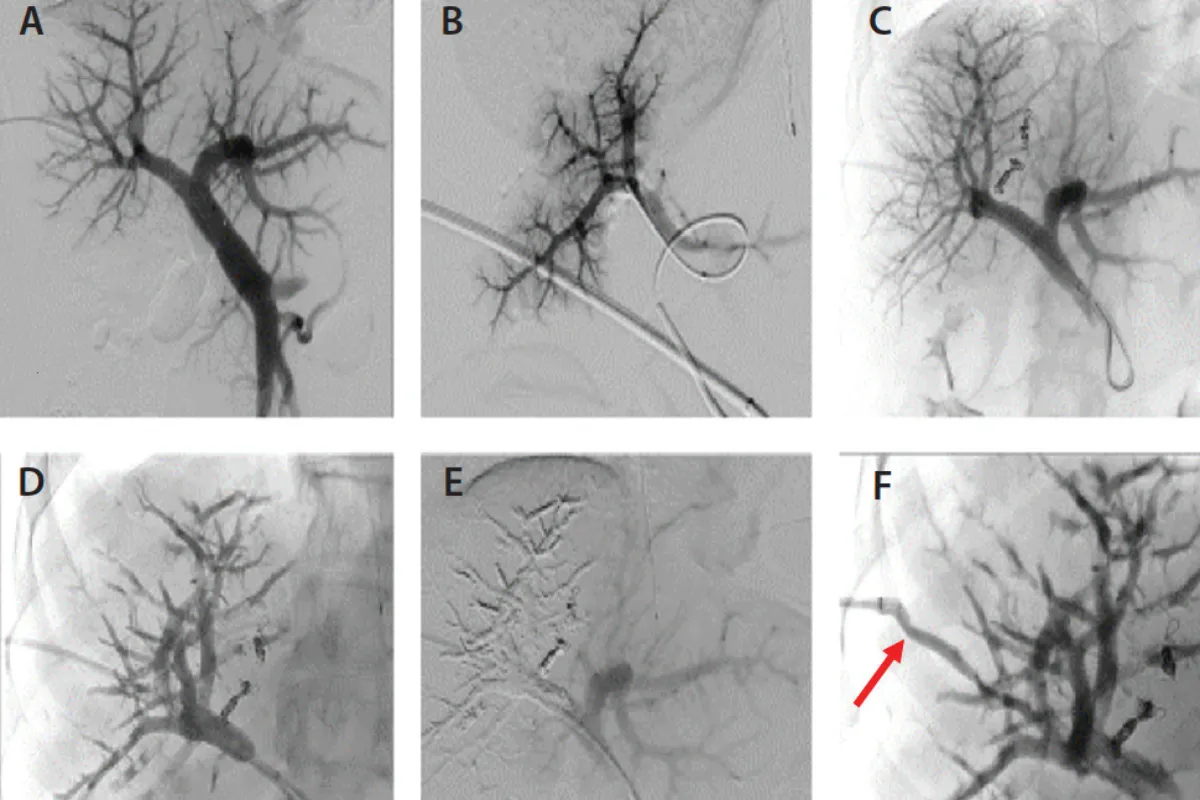
This procedure blocks a branch of the portal vein to redirect blood flow and stimulate growth of the future liver remnant. It helps prepare patients for safer liver surgery by increasing healthy liver volume.
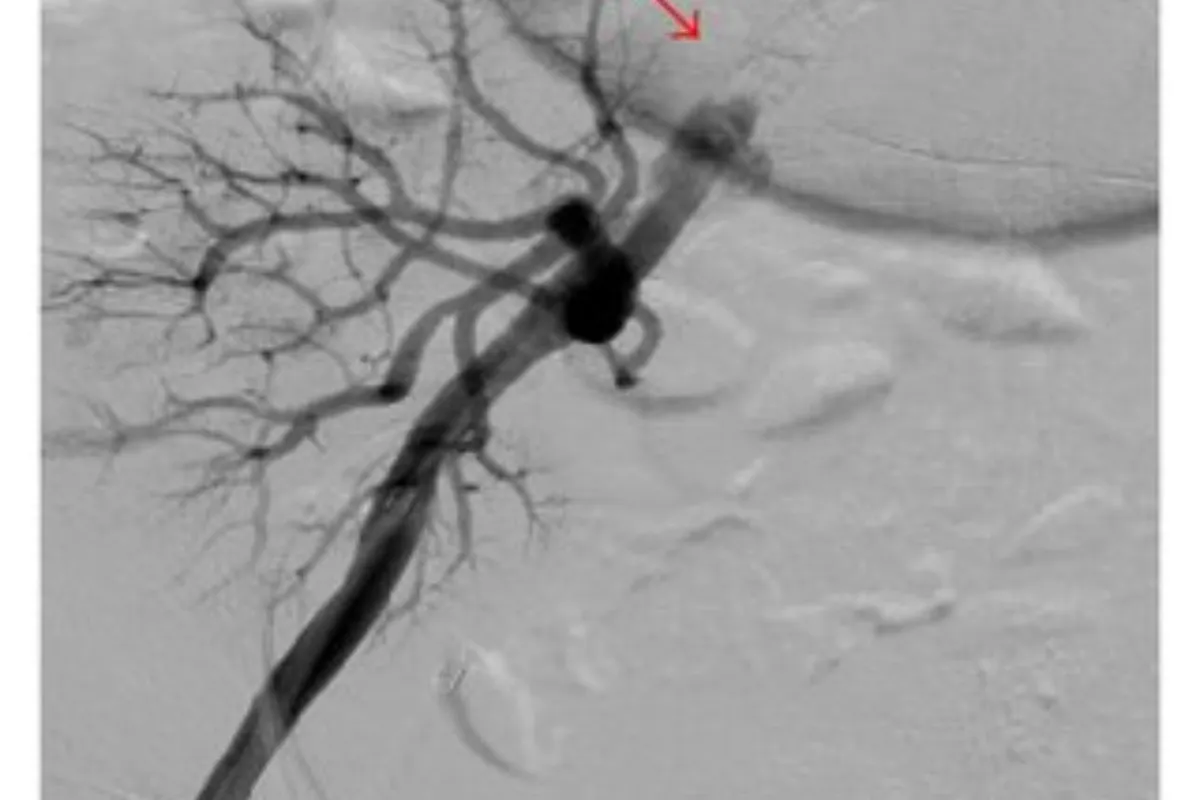
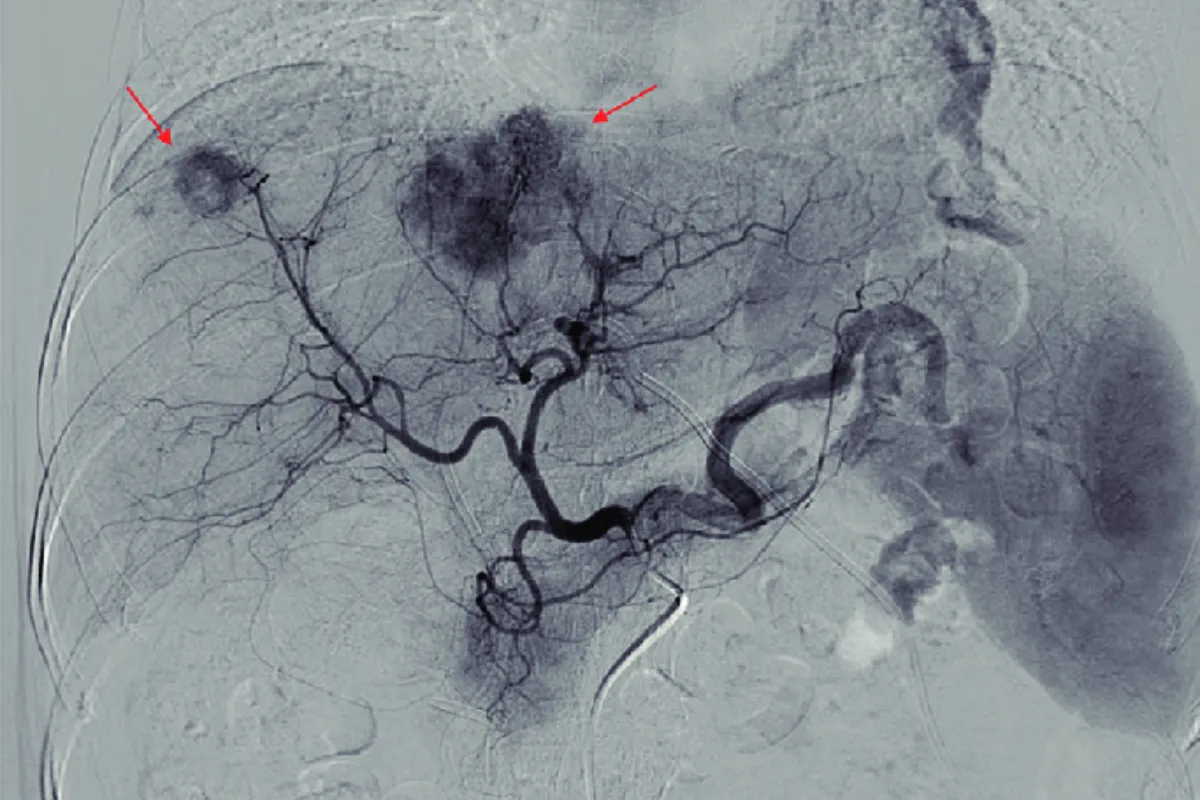
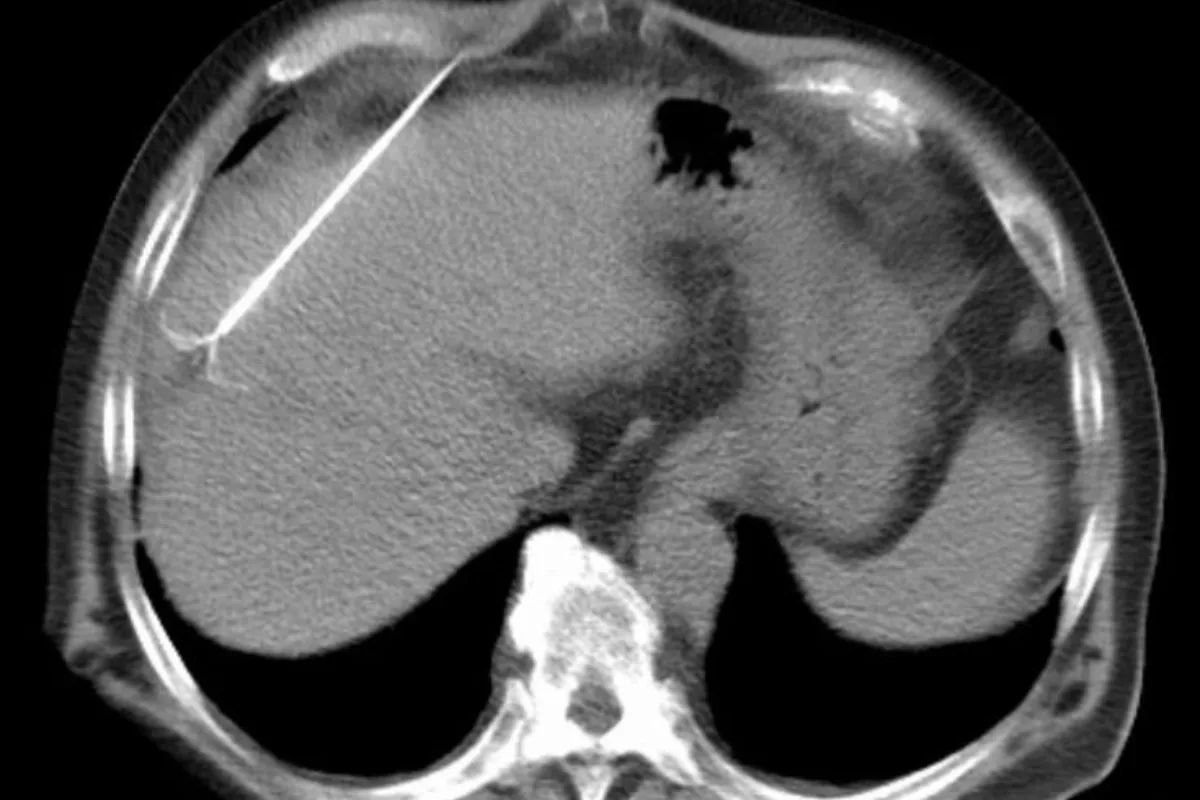
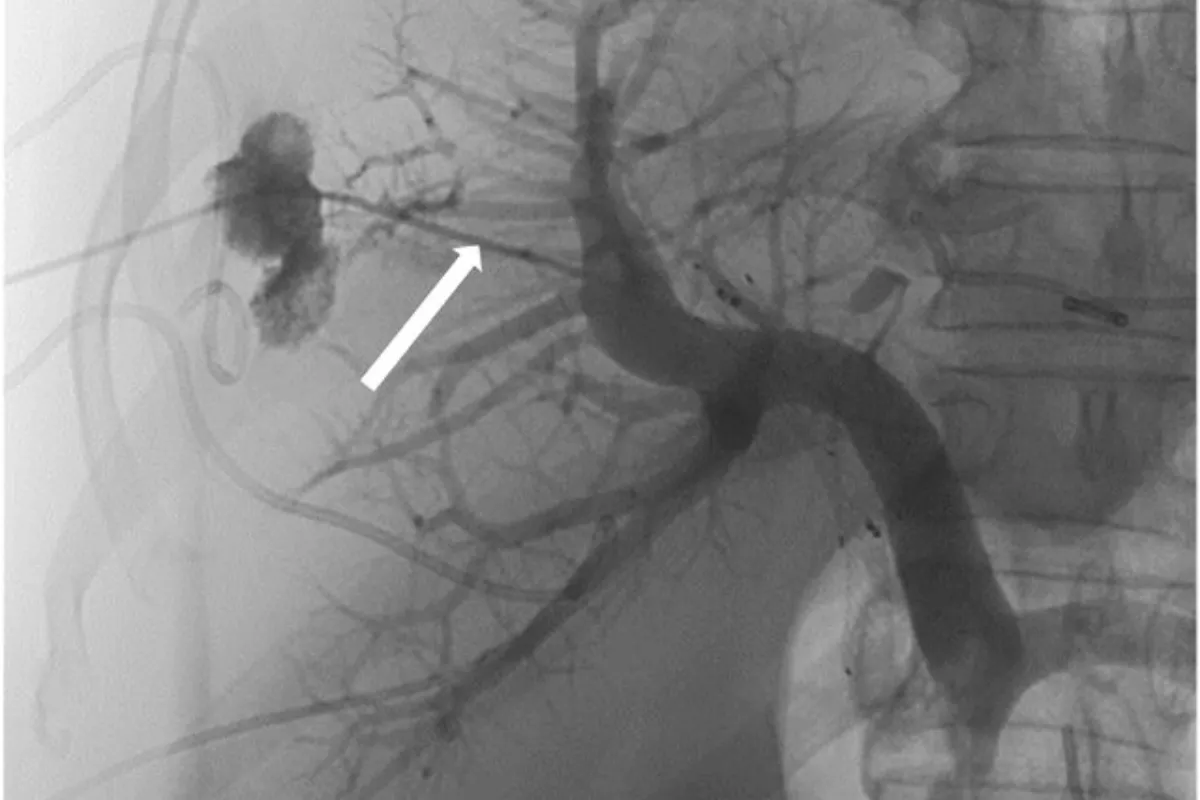
These targeted procedures block abnormal or bleeding vessels to control hemorrhage and shrink problematic tissues. They are minimally invasive, effective, and help avoid major surgery while restoring normal blood flow patterns.
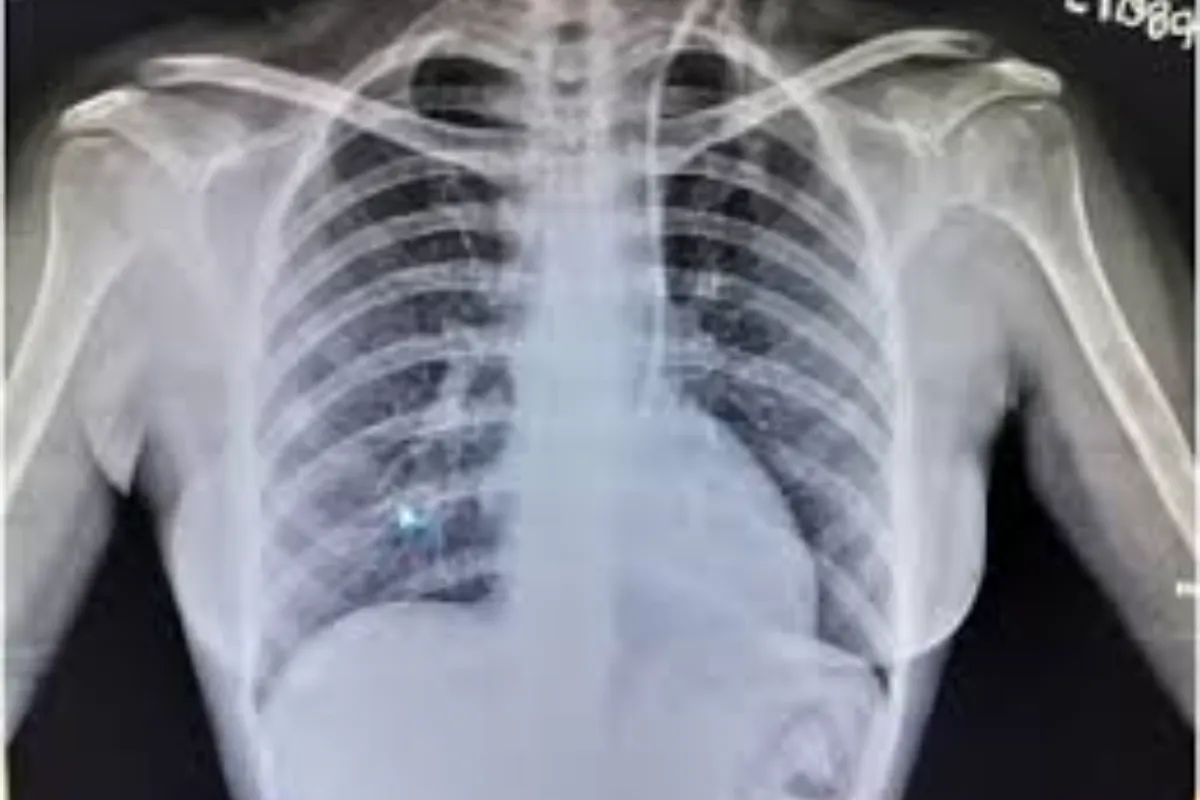
A dialysis catheter is placed into a large vein to provide reliable access for hemodialysis. It allows efficient blood filtration and is used when immediate or long-term dialysis support is needed.
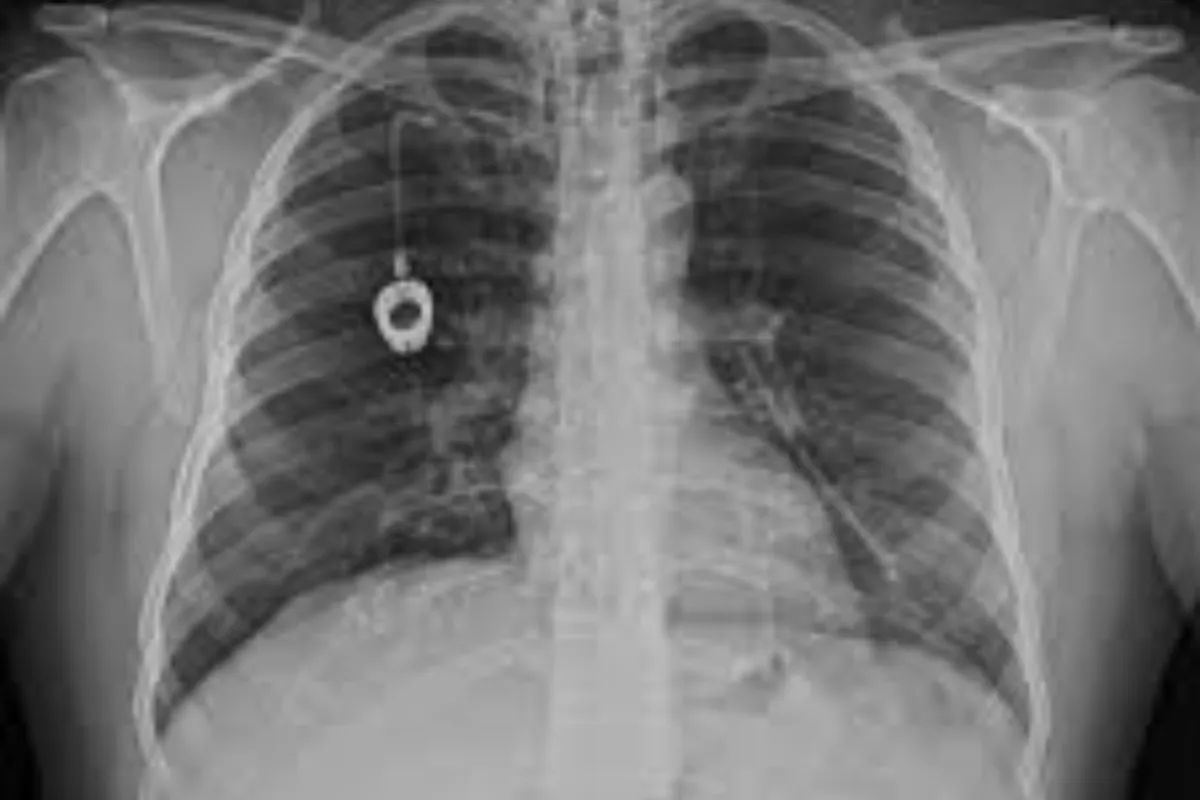
A chemoport is a small device placed under the skin to provide easy, long-term access for chemotherapy. It makes treatment safer, reduces repeated needle pricks, and improves patient comfort during therapy.
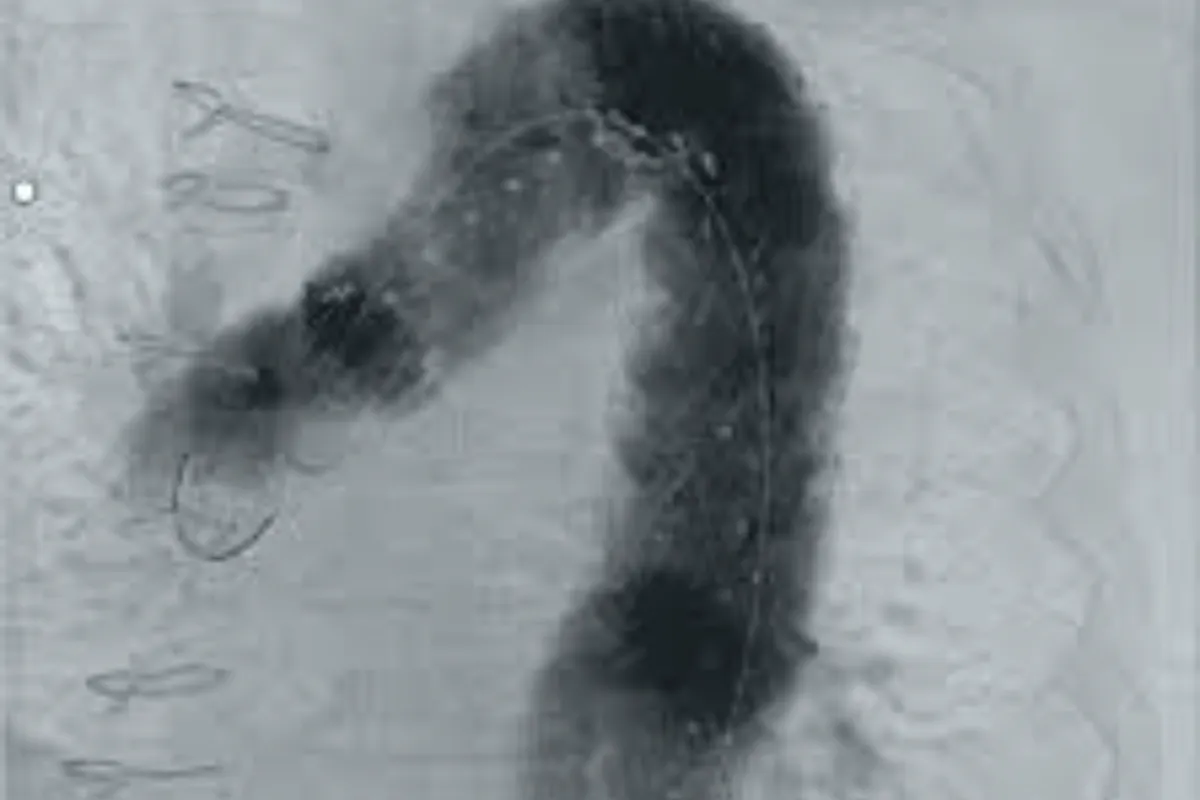
A minimally invasive procedure used to treat aneurysms or tears in the thoracic aorta by placing a stent-graft inside the vessel. It strengthens the weakened segment, prevents rupture, and allows faster recovery compared to open surgery.
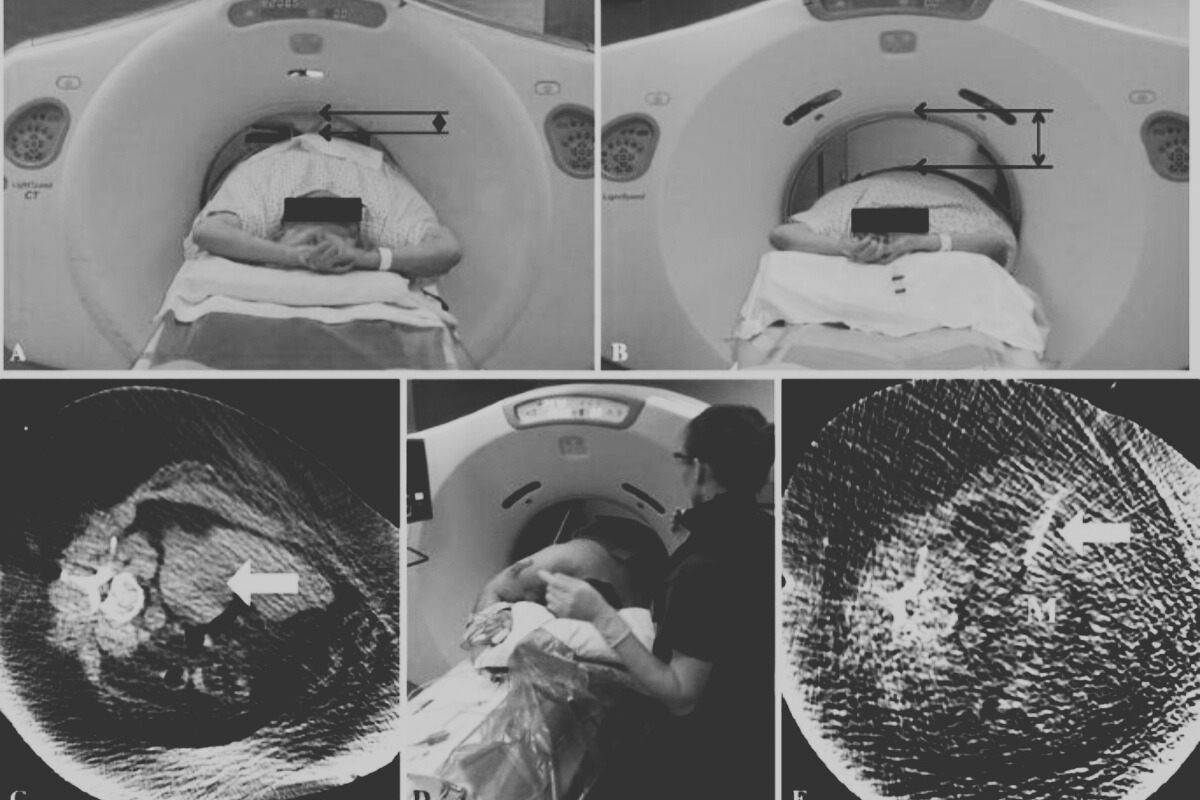
A per-abdominal biopsy is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin needle to take a small tissue sample through the abdomen, usually with ultrasound or CT guidance. It helps diagnose conditions like infections, tumors, or organ diseases in the liver, kidney, or other abdominal areas. The procedure is quick, done with local anesthesia, and generally safe with minimal discomfort.
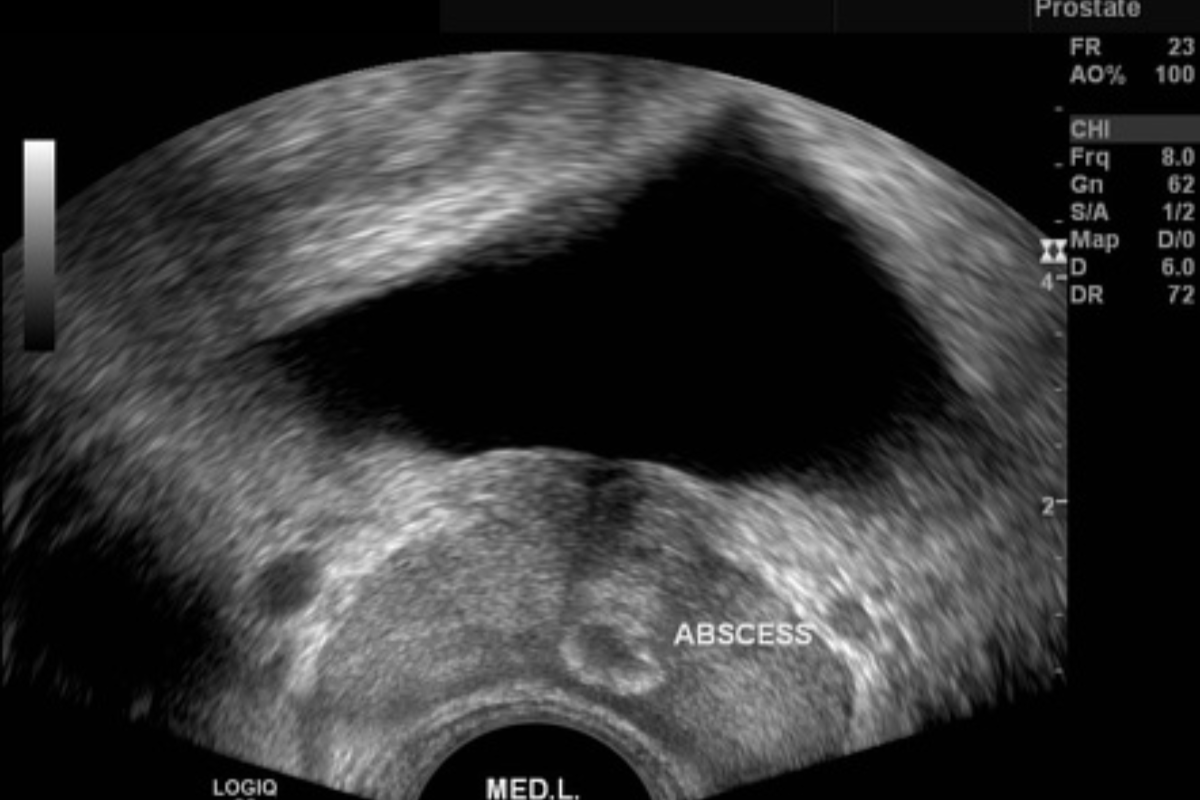
TRUS (Transrectal Ultrasound) is a procedure in which a small ultrasound probe is gently inserted into the rectum to create clear images of the prostate and nearby tissues. It is commonly used to diagnose prostate problems, guide prostate biopsies, and assess abnormalities. The test is quick, safe, and usually causes only mild discomfort.
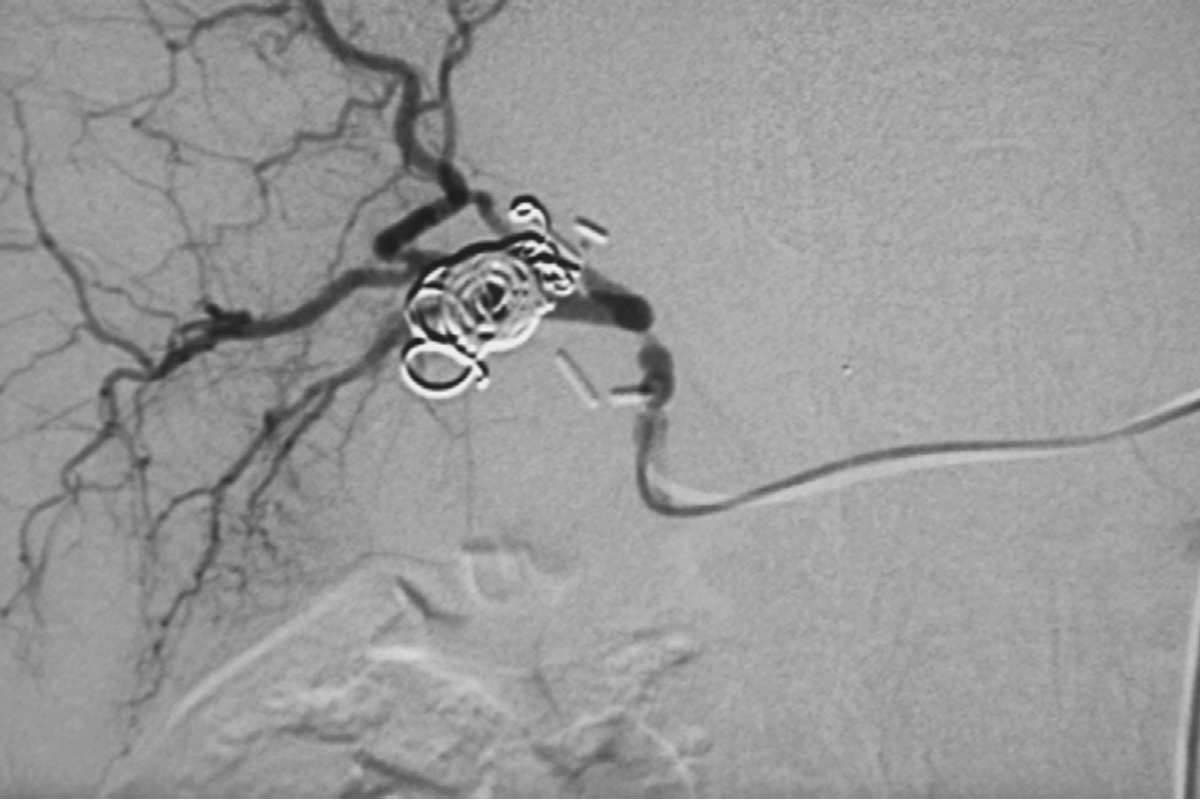
Coil embolisation is a minimally invasive treatment in which a doctor inserts a thin catheter into a blood vessel and places tiny metal coils at the bleeding site. These coils block the blood flow and help stop the GI bleeding quickly and safely. It is often used when endoscopy cannot control the bleeding.
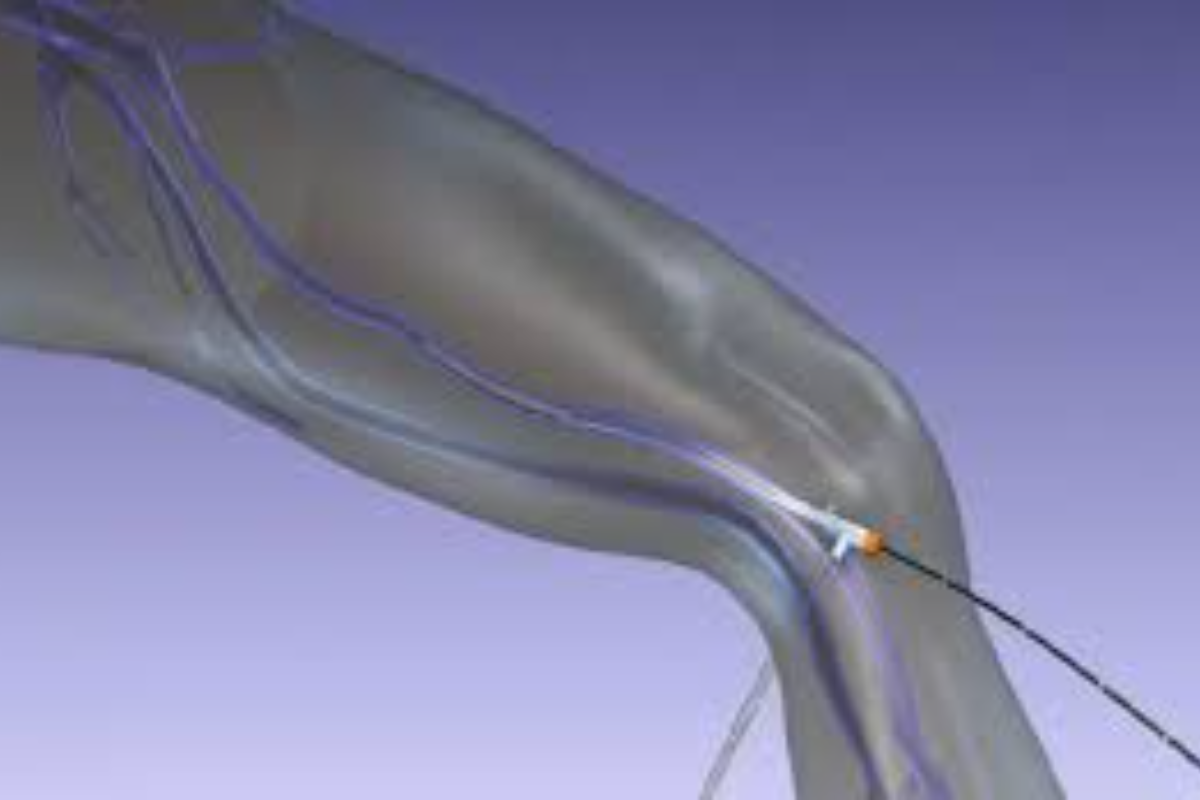
These advanced minimally invasive methods close abnormal veins to improve blood flow and reduce symptoms. They provide quick recovery, less pain, and better cosmetic results compared to conventional surgery.
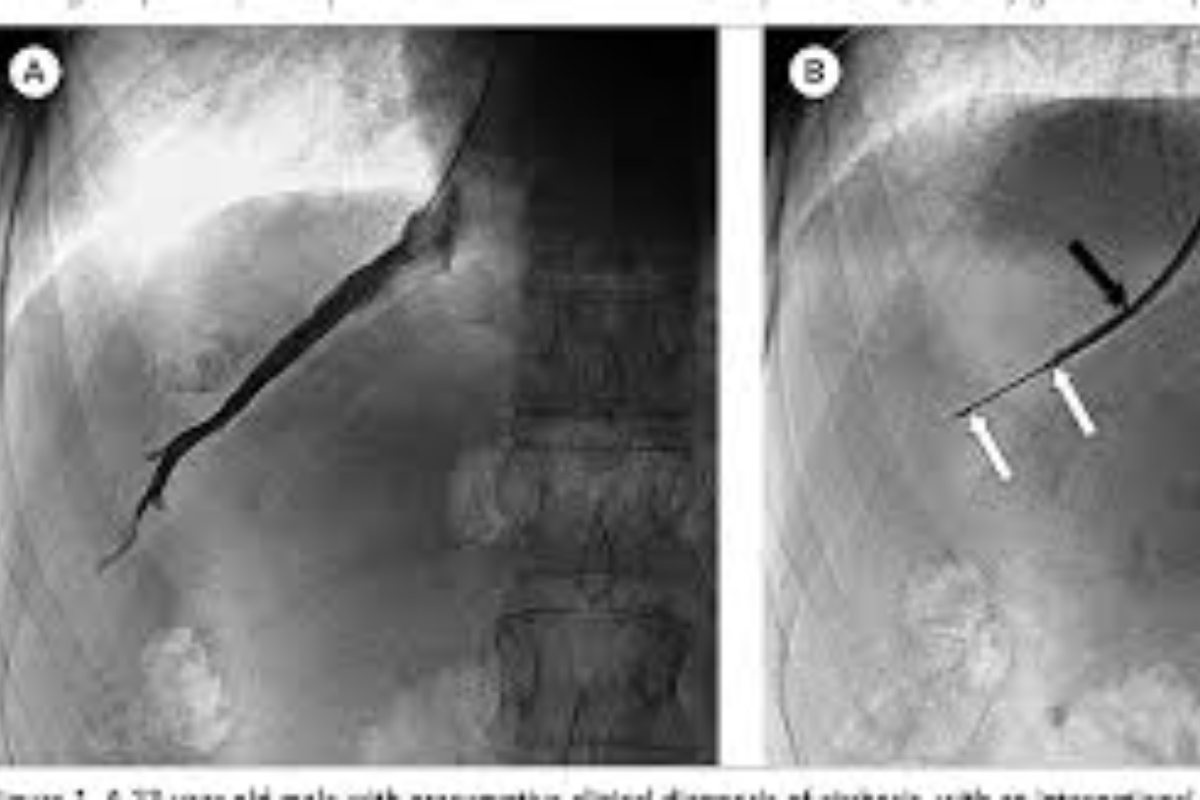
Transjugular Liver Biopsy is a procedure where a liver tissue sample is taken through a vein in the neck using a thin catheter. It is mainly done for patients who have bleeding risks or abdominal fluid, offering a safer alternative to traditional liver biopsy.
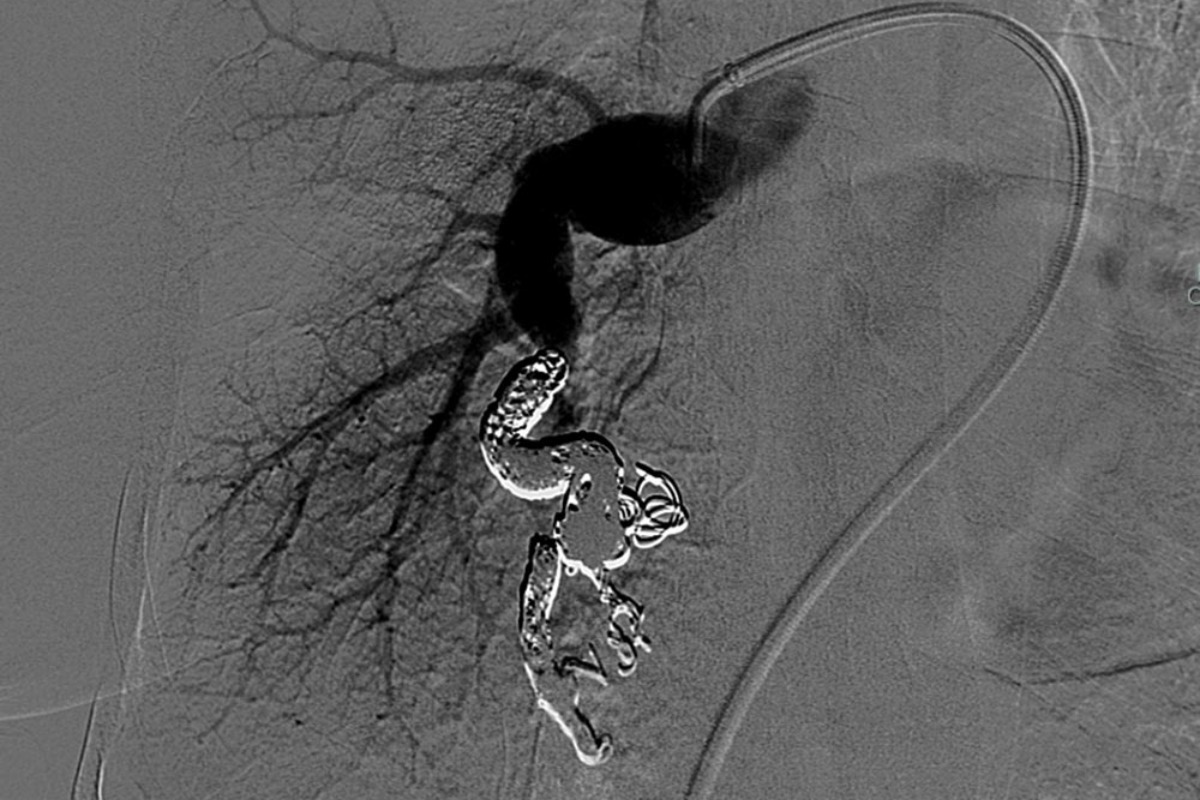
Vascular Malformation Treatment refers to medical procedures used to treat abnormal clusters of blood vessels. These treatments may include embolisation (blocking abnormal vessels), laser therapy, injections, or surgery—depending on the type and location of the malformation. The goal is to reduce symptoms, prevent bleeding, and improve appearance or function.
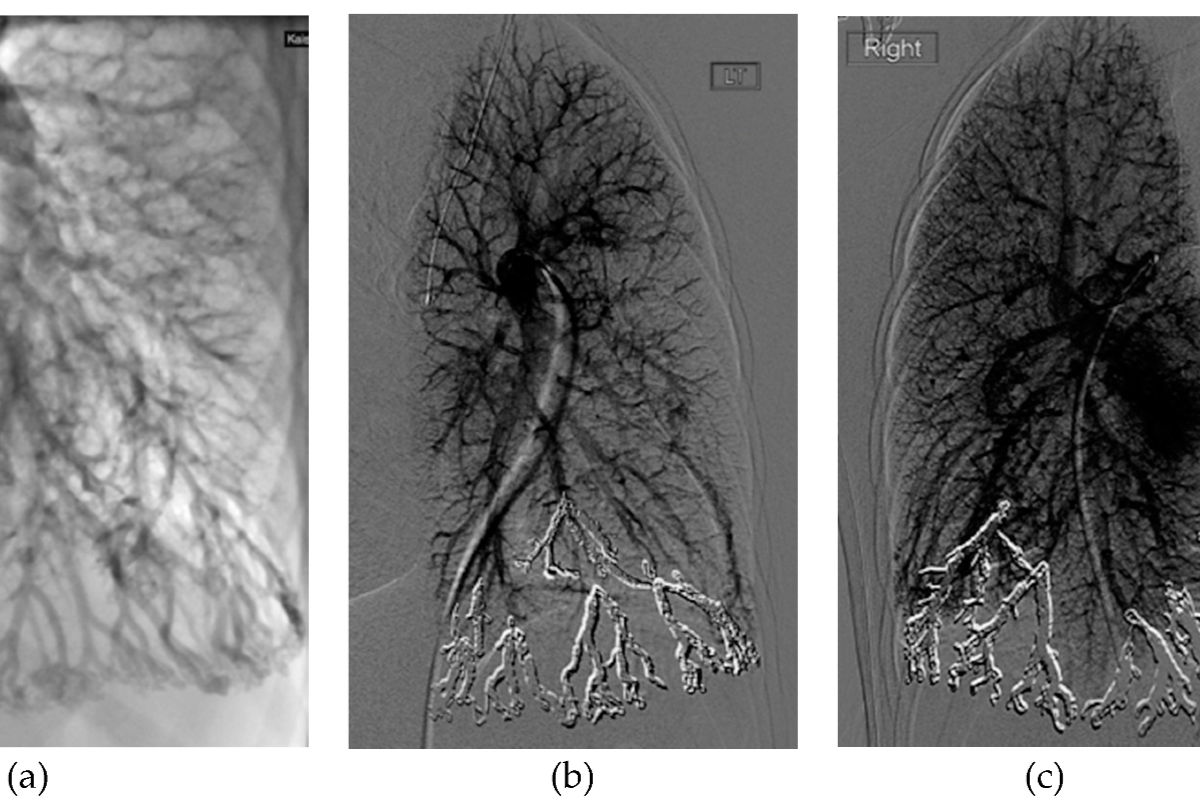
Pulmonary AVF Treatment involves closing an abnormal connection between a lung artery and vein (pulmonary arteriovenous fistula). Doctors usually treat it with embolisation, where a catheter is used to place coils or plugs to block the abnormal vessel. This improves oxygen levels, prevents complications, and is a minimally invasive, safe procedure.
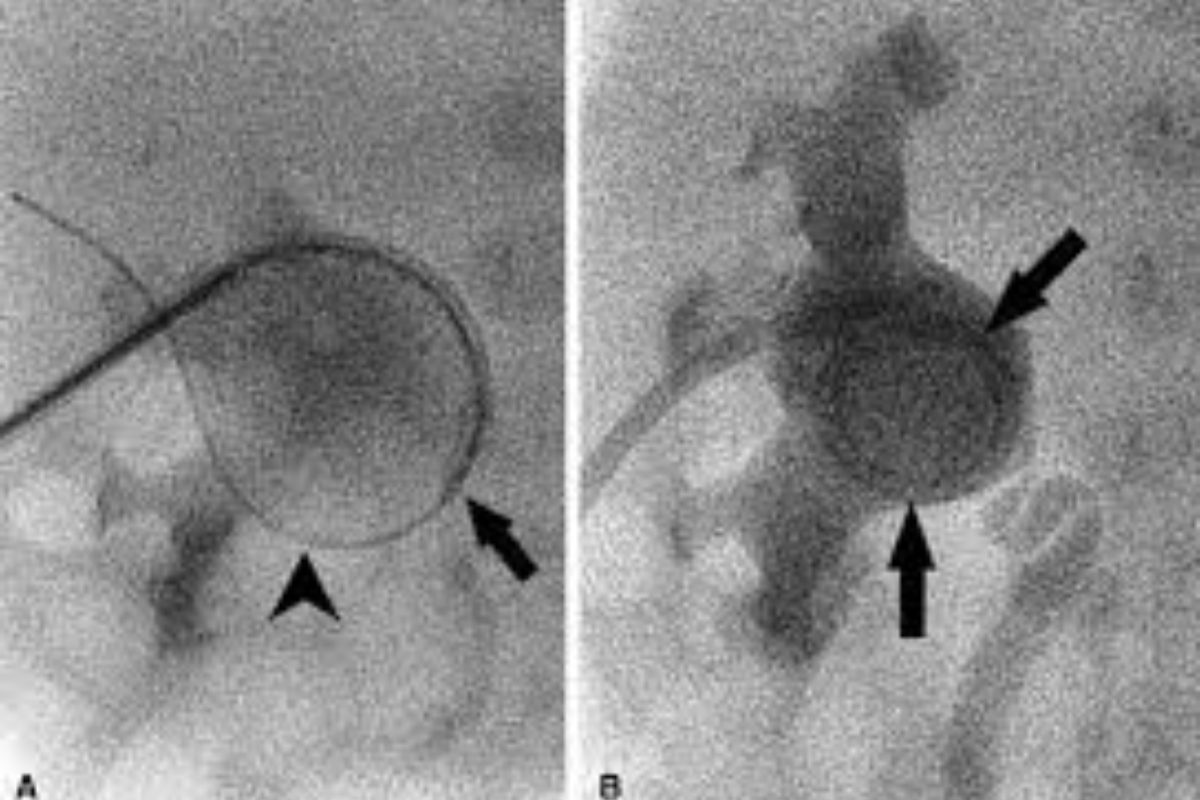
Percutaneous Nephrostomy is a procedure where a thin tube is inserted through the skin into the kidney to drain urine. It is done when the normal urinary pathway is blocked due to stones, tumors, or infection. This helps relieve pain, prevent kidney damage, and allow proper urine flow.
Your primary care physician or specialist refers you to an interventional radiologist based on your condition.
Meet with the interventional radiologist to discuss your condition, treatment options, and procedure details.
Follow specific instructions regarding medications, fasting, and other preparations before your procedure.
The minimally invasive procedure is performed, typically taking 30 minutes to 2 hours depending on complexity.
Brief monitoring period followed by discharge instructions for at-home care and follow-up appointments.
Want to consult with our vascular specialists? Book an appointment online or call us directly.
sardavascularcenter@gmail.com
+91 xxxxxxxx
Dehradun, Uttarakhand, 248001

IR uses tiny incisions (often just needle punctures) rather than large surgical openings. This results in less pain, lower risk of complications, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional surgery.
Most IR procedures cause minimal discomfort. Local anesthesia is used to numb the area where the catheter or needle is inserted. Patients may feel pressure but typically not sharp pain during the procedure.
Recovery time varies by procedure but is generally much faster than traditional surgery. Many patients go home the same day or after an overnight stay. Most can resume normal activities within a few days to a week.
IR can treat a wide range of conditions, including vascular diseases, cancers, uterine fibroids, back pain, kidney stones, liver disease, and many more. New applications are continually being developed as technology advances.
© 2025 Sarda Vascular Centre. All Rights Reserved.